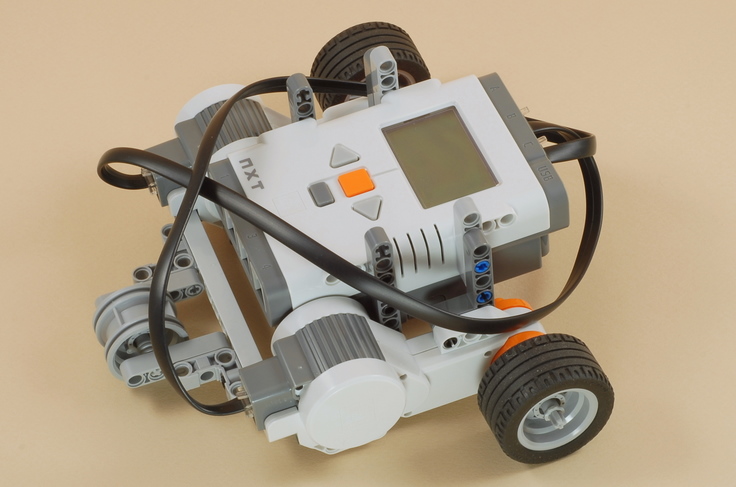
My partner Jill Swan and I did the pulley lab together. The lab consisted of exploring Newton’s 2nd Law- the law of conservation of energy, velocity and acceleration, and power. We used the Lego Mindstorm robot to see how acceleration changed when mass changed and power was fixed and when power changed and mass was fixed.
Does the acceleration vary with mass? Yes. When we changed the masses- .05 kg, .1 kg, .15 kg, .2 kg, and .25 kg, with the power level left constant at 75, the acceleration decreased. The first graph is a representation of our results. It shows the trend line angled in a downward slope in regards to acceleration vs. mass.
Does the acceleration vary with power level? Yes. When we changed the power level- 50, 60, 70, 80, and 90, with the mass left constant at .1 kg, the acceleration level increased. The second graph is a representation of our results. It shows the trend line angled in an upward slope in regards to power vs. acceleration.
Is the linear trend line as expected? Yes. The linear trend line reflected what I expected the results to be based on the lecture and understanding the formula F=ma.
17.5 cm- to bottom of pulley
9 cm- height of weights