What is the energy grid?- The energy grid, or power grid in the United States is the system by which electricity is distributed to consumers across the country. The grid connects the energy producers and the consumers through a complex electrical system composed of three interconnected systems.
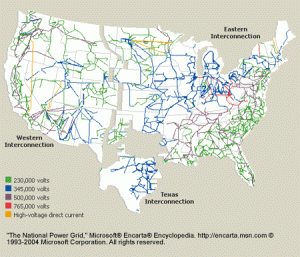
What composes the infrastructure of the energy grid?- As stated above the energy grid is composed of three interconnected systems. The systems are divided into the Western Interconnection, the Eastern Interconnection and the Texas Interconnection. According to the US Energy Information Administration, “The interlinked systems now include about 2,000 electric distribution utilities, more than 300,000 miles of transmission and distribution lines, millions of customers, and 7,000 power plants.” The image below is a graphic representation of the energy grid, showing the three interconnections.
How does the energy grid work?- The first step of the grid is the power source, whether that be a from a renewable source such as a hydro-electric plant or a non-renewable source such as a coal plant. Once the power is generated, it is stepped up at a transmission substation in order to be able to travel long distances. In order for the power to be used, it comes off the transmission grid to the distribution grid where it is stepped down at a distribution substation. On the distribution grid it is then stepped down a second time through the transformers so the power is now at the 120 or 240 Volts that we use in our homes and businesses.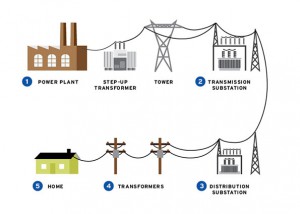 What are Smart Grids?- Smart grids are a way of modernizing the power grid by adding technology to the current grid such as meters, sensors, and synchrophasors. This incorporation of digital technology enables communication between the grid, consumers, and the operating network providing data on consumption, voltage, damage, and potential problems among others. According to the US Energy Information Administration, “A smarter grid makes the electrical system more reliable and efficient by helping utilities reduce electricity losses and to detect and fix problems more quickly. The smart grid can help consumers conserve energy, especially at times when demand reaches significantly high levels or when an energy demand reduction is needed to support system reliability.”
What are Smart Grids?- Smart grids are a way of modernizing the power grid by adding technology to the current grid such as meters, sensors, and synchrophasors. This incorporation of digital technology enables communication between the grid, consumers, and the operating network providing data on consumption, voltage, damage, and potential problems among others. According to the US Energy Information Administration, “A smarter grid makes the electrical system more reliable and efficient by helping utilities reduce electricity losses and to detect and fix problems more quickly. The smart grid can help consumers conserve energy, especially at times when demand reaches significantly high levels or when an energy demand reduction is needed to support system reliability.”
Pros:
1. Provides power to the country
2. Contributes to the economy in ways such as providing jobs anywhere from at the power plants to the installation of new lines.
Cons:
1. Security threats: “In fiscal year 2014, there were 79 hacking incidents at energy companies that were investigated by the Computer Emergency Readiness Team, a division of the Department of Homeland Security. There were 145 incidents the previous year.” CNN
2. Siting new transmission lines when there is opposition to construction.
3. Reaching renewable energy generation sites can be challenging.
References:
1. US Energy Information Administration: http://www.eia.gov/energy_in_brief/article/power_grid.cfm
2. CNN: http://money.cnn.com/2014/11/18/technology/security/energy-grid-hack/
3. How Stuff Works: http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/energy/power4.htm
4. Office of Electricity Delivery & Energy Reliability: http://energy.gov/oe/services/technology-development/smart-grid





 What are Smart Grids?- Smart grids are a way of modernizing the power grid by adding technology to the current grid such as meters, sensors, and synchrophasors. This incorporation of digital technology enables communication between the grid, consumers, and the operating network providing data on consumption, voltage, damage, and potential problems among others. According to the US Energy Information Administration, “A smarter grid makes the electrical system more reliable and efficient by helping utilities reduce electricity losses and to detect and fix problems more quickly. The smart grid can help consumers conserve energy, especially at times when demand reaches significantly high levels or when an energy demand reduction is needed to support system reliability.”
What are Smart Grids?- Smart grids are a way of modernizing the power grid by adding technology to the current grid such as meters, sensors, and synchrophasors. This incorporation of digital technology enables communication between the grid, consumers, and the operating network providing data on consumption, voltage, damage, and potential problems among others. According to the US Energy Information Administration, “A smarter grid makes the electrical system more reliable and efficient by helping utilities reduce electricity losses and to detect and fix problems more quickly. The smart grid can help consumers conserve energy, especially at times when demand reaches significantly high levels or when an energy demand reduction is needed to support system reliability.”