Solar Leaf

Daniel Nocera and his research team at MIT have developed the first “artificial leaf.” Made from a thin silicon solar cell, the leaf is dropped into water where it separates hydrogen and oxygen molecules that are collected and connected to fuel cells that produce electricity. The leaves can’t collect energy as efficiently as traditional solar PVs, but are incredibly cheap to make.
The leaf could bring electricity cost effectively, especially in developing countries, to households that aren’t connected to energy grids.
Eliodomestico Solar Still

Italian designer Gabriele Diamanti created solar household still for developing countries with limited or no access to fresh drinking water. To make it work you pour seawater through the opening at the top, and the sun heats it during the day. The pressure forces steam through the nozzle leading to a watertight boiler, and condenses against the lid. The Eliodomestico provides up to 5 liters of water a day.
Since the sun does all the work, there are no operating costs. The still is even made entirely of inexpensive from available materials.
LuminAID Light

Anna Stork and Andrea Sreshta, the founders of LuminAID, created this solar-inflatable light in response to Haiti’s January 2010 earthquake. It’s designed specifically for those affected by disasters, crises and conflicts. The LuminAID light packs flat — 50 lights take up the same space as eight regular flashlights — and inflates to become a lantern and to reduce the glare of the powerful LED bulbs. Within the past year, the LuminAID light has been used in humanitarian relief aid in the wake of disasters such as Hurricane Isaac and Hurricane Sandy.
Portable Light Project

The Portable Light Project enables people in developing countries to create energy-harvesting textiles, which they can adapt to their own needs. For example, locals can weave the flexible photovoltaic cells into bags they carry around during the day, harvesting sunlight, and open it up to light their homes at night. Developed by Boston-based architecture firm KVA MATx, each kit includes a textile reflector, a photovoltaic material, a battery case with a USB port and an LED light. The battery charges in six hours, providing over 20 hours of light. The Portable Light Project has launched projects in Nicaragua, Mexico, Venezuela, South Africa, Kenya, Haiti and Brazil.
"New Solar Innovations That Could Change The World." Mosaic. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Feb. 2016.
"Ingenious Solar Projects Impacting the Developing World." Mashable. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Feb. 2016
"Concentrated Solar Power." World Bank. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Feb. 2016.
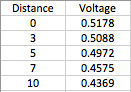



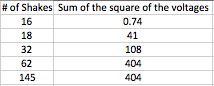
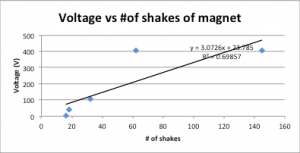
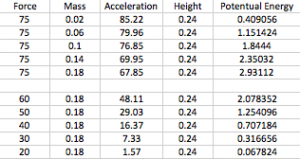
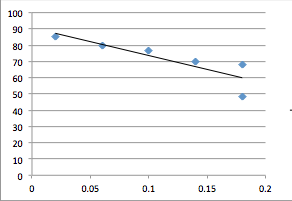
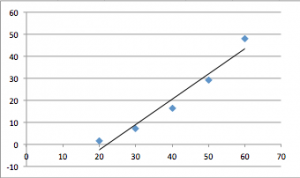 On the second diagram Force*Acceleration. With the bigger force, acceleration is bigger as well.
On the second diagram Force*Acceleration. With the bigger force, acceleration is bigger as well.