Stirling Engine
Robert Sterling invited the sterling engine in 1816. It uses the Sterling Cycle, which is different is from the cycles found in internal-combustion engines. Inside the engine, there are no exhaust valves, no explosions taking place and no gasses leaving. The cycle can be powered by any source of heat, from gasoline to coal to decaying plants. Currently, sterling engines are a rarity but scientist are working on developing a mass-market use for the engine.
If you have a cylinder with gas inside and you compress it (decrease the volume of its space), the temperature of that gas will increase. Also, if you have the same amount of gas and you raise the temperature instead of compressing it, its pressure will increase. These concepts are crucial when explaining how the sterling engine works. There are 4 parts to the cycle:
- Heat is added to the gas inside the left cylinder (heated), which causes pressure to build and the piston to push down.
- Both pistons work in sync so while the left piston moves down, the left piston moves up which pushes the gas into a right cylinder (cooled). When the gas is cooled, its pressure is lowered which makes it easier to compress.
- The piston in the right cylinder compresses the gas and generates heat, which is removed by whatever cooling source there is.
- As the left piston moves down, the right piston moves up. Which pushes the gas into the left cylinder (heated) where it builds pressure and this is when the cycle repeats.
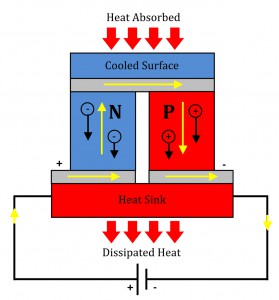
The Peltier effect
Discovered by French physicist Jean-Charles Athanase Peltier, it is an effect whereby heat is emitted or absorbed when an electric current passes across a junction between the two materials. In other words, the Peltier effect is a temperature difference that is created by Appling electricity between two electrode that are connected to a sample of semiconductor material which is used to transfer heat.
In the device, the electrodes are made of metal and the semiconductor material creates two junctions between different materials, which, creates a pair of thermocouple voltage which is applies to the electrodes to force electricity through the semiconductor. In general, the devices are used for thermoelectric cooling in electronics and computers
Sources:
https://van.physics.illinois.edu/qa/listing.php?id=19853
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermoelectric_cooling
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/Peltier-effect
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9Cuh2msd2lo
http://auto.howstuffworks.com/stirling-engine1.htmhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stirling_enginehttp://www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/351/oldslides/Lecture11.pdf