Electricity Generation:
How does a coal power plant work? The process begins when coal is ground to a powder. It is then blown into a boiler where the coal dust is burned, thus creating heat energy. Why grind the coal? Grinding it into a powder creates more surface are which, in turn, allows for faster and hotter burning producing more heat and less waste. The burning of the coal heats water in pipes coiled around the boiler, turning it into steam. Pressure is created by keeping the steam in pipes where it expands and the pressure drives the steam over the blades of a steam turbine. The steam turbine spins and mechanical energy is produced. A shaft connects the steam turbine to the turbine generator, so as the steam turbine spins, the generator does as well. Using an electromagnetic field, the generator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The byproducts are ash and exhaust gas. The ash is collected from the bottom of the boiler and often sold to be used in building materials and the gases enter the exhaust stack. The exhaust stack has filters to remove the dust and ask before the gas is released into the air. How does a natural gas power plant work? The first step at a natural gas power plant is pumping the natural gas into the turbine. There it is mixed with air and burned, creating heat energy. Combustion gas is also created. The heat causes the combustion gas to expand causing a buildup of pressure. The pressure drives the combustion gas over the blades of the gas turbine, causing it to spin, converting some of the heat energy into mechanical energy. A shaft connects the gas turbine to the gas turbine generator so when the turbine spins, the generator spins as well. Using an electromagnetic field, the generator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The combustion gas is then piped to the heat recovery steam generator where it is used to heat pipes of water, turning the water to steam, before leaving through the exhaust stack. The hot steam expands in the pipes and emerges under high pressure. These high-pressure steam jets spin the steam turbine. The steam turbine is connected by a shaft to the steam turbine generator, which converts the turbine’s mechanical energy into electrical energy.
How does a natural gas power plant work? The first step at a natural gas power plant is pumping the natural gas into the turbine. There it is mixed with air and burned, creating heat energy. Combustion gas is also created. The heat causes the combustion gas to expand causing a buildup of pressure. The pressure drives the combustion gas over the blades of the gas turbine, causing it to spin, converting some of the heat energy into mechanical energy. A shaft connects the gas turbine to the gas turbine generator so when the turbine spins, the generator spins as well. Using an electromagnetic field, the generator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The combustion gas is then piped to the heat recovery steam generator where it is used to heat pipes of water, turning the water to steam, before leaving through the exhaust stack. The hot steam expands in the pipes and emerges under high pressure. These high-pressure steam jets spin the steam turbine. The steam turbine is connected by a shaft to the steam turbine generator, which converts the turbine’s mechanical energy into electrical energy.
How does a nuclear power plant work? The nuclear power plant begins the process in a reactor vessel- a tough steel capsule that houses the fuel rods, sealed metal cylinders containing pellets of uranium oxide. When a neutron, a neutrally charged subatomic particle, hits a uranium atom, the atom sometimes splits, releasing two or three more neutrons. This process converts the nuclear energy that binds the atom together into heat energy. When atoms in the fuel split, the neutrons they release are likely to hit other atoms and make them split as well creating a chain reaction producing large amounts of heat. Water flows through the reactor vessel, where the chain reaction heats it to around 300°C. The water needs to stay in liquid form for the power station to work, so the pressuriser stops it from boiling. The reactor coolant pump circulates the hot pressurised water from the reactor vessel to the steam generator. Here, the water flows through thousands of looped pipes before circulating back to the reactor vessel. A second stream of water flows through the steam generator, around the outside of the pipes. This water is under much less pressure, so the heat from the pipes boils it into steam. The steam then passes through a series of turbines, causing them to spin, converting the heat energy produced in the reactor into mechanical energy. A shaft connects the turbines to a generator, so when the turbines spin, so does the generator. The generator uses an electromagnetic field to convert this mechanical energy into electrical energy.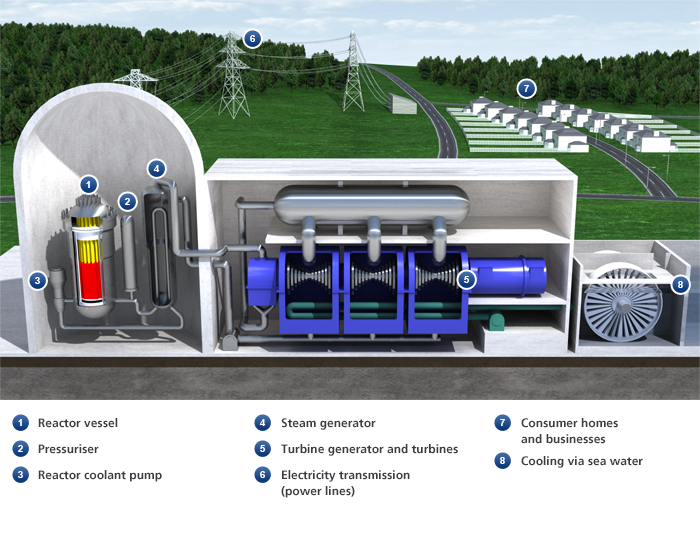 There are similarities in the three types of power plants. They all use hot water, steam, turbines, and electromagnetic fields in their production process. There are a couple big differences I think are worth mentioning- the ability to control when and how much power is made and environmental impact. While nuclear power plants are in full effect at all times, natural gas and coal production can increase and decrease as needed to meet the demands, a definite benefit. On the note of environmental efficiency, nuclear is the clear winner producing carbon-free electricity as well as being a renewable resource. Natural gas produces less greenhouse gases than coal, about half as much, but the goal should eventually be no gas emissions so natural gas is not a perfect solution. It is abundant and cheap at the moment making it an appealing source of energy for now.
There are similarities in the three types of power plants. They all use hot water, steam, turbines, and electromagnetic fields in their production process. There are a couple big differences I think are worth mentioning- the ability to control when and how much power is made and environmental impact. While nuclear power plants are in full effect at all times, natural gas and coal production can increase and decrease as needed to meet the demands, a definite benefit. On the note of environmental efficiency, nuclear is the clear winner producing carbon-free electricity as well as being a renewable resource. Natural gas produces less greenhouse gases than coal, about half as much, but the goal should eventually be no gas emissions so natural gas is not a perfect solution. It is abundant and cheap at the moment making it an appealing source of energy for now.
References:
1. EDF Energy- Coal
http://www.edfenergy.com/energyfuture/coal-generation
2. EDF Energy- Natural Gas
http://www.edfenergy.com/energyfuture/generation-gas
3. EDF Energy- Nuclear Power
http://www.edfenergy.com/energyfuture/generation-nuclear
4. Oil Price
http://oilprice.com/Alternative-Energy/Nuclear-Power/Natural-Gas-Threatens-U.S.-Nuclear-Future.html
