Explanation
The solar energy experiment allowed us to understand the implementation of photovoltaic cells. “Photovoltaic is the name of a method of converting solar energy into direct current electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon commonly studied in physics, photochemistry and electrochemistry.”
Solar energy has become extremely popular according to renewableenergyworld.com, “The solar panel is becoming an increasingly popular form of alternative energy around the world, using photovoltaic and silicon solar cells to convert radiation into power. Solar power has had a long history of failed starts and limited distribution. As an alternative to the burning of fossil fuels, solar panels rank alongside wind and hydropower as essential energy options for the future of the planet, and offer the additional benefit of being easier to integrate into the home.”
The experiment in class allowed us to see how voltage has an effect on distance and by using colored filters (red, blue and green) we were able to see how this would change the voltage. Our professor discussed about the source of light where the closer the panel is to the light then a better result of voltage would be presented. We once again used the Lego NXT robot, the colored filters as mentioned before, the Labview program, Excel, a ruler and a solar cell.
By using the colored filters we were able to measure which one allowed the highest amount of voltage. Each color had a different result. The other stage of the experiment consisted of us holding the flashlight at different distances from the solar cell using several attempts to get a variety of results. Our results displayed that when the voltage decreased the distance between the flashlight and the solar cell was further and increased as the flashlight was closer to flashlight.
Results
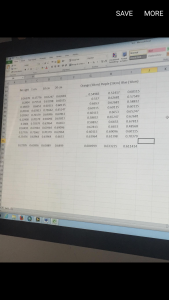
Our results had a slight issue due to the LabView reading at 1cm. Meaning our results are not as accurate as they should be.
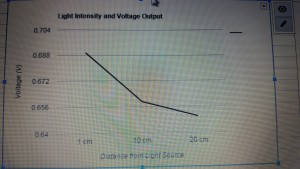
Our first test was voltage with no source of light. The result produced was 0.22505. We next used the flashlight and the solar sensor, we used the measurements of 1cm, 10cm and 20cm. Like mentioned before the voltage was decreasing the closer it was from the light source. Our results were 0.68954 V (1 cm), 0.65889 V (10 cm) and 0.6499 V (20 cm)
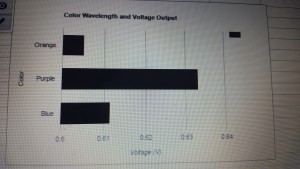
The other part of the experiment was running the LabView program for another three times. We now used the filters. They all produced a similar result with Orange (0.60499 V), Purple (0.63323 V) and Blue (0.61141 V).
Below is our graph.
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/ugc/blogs/2012/09/the-growing-popularity-of-solar-panels.html
You have a real ability for writing unique content. I like how you think and the way you represent your views in this article. I agree with your way of thinking. Thank you for sharing. Healthy Marriage
Hi there, I found your blog via Google while searching for such kinda informative post and your post looks very interesting for me. Guest Posting
Looking for free bingo games?Join the ultimate online bingo experience with Bingo Cash ! Test your skills to compete against players in real time. Join now and bingo for cash!
Solar energy, with the use of solar panels and photovoltaic cells, has indeed gained popularity as a sustainable and clean alternative energy infinite craft source. The mention of its history and the comparison with other renewable energy options like wind and hydropower highlights its significance in the quest for environmentally friendly energy solutions.
Your willingness to consider multiple perspectives helps foster understanding. Solar
Cheers for this kind of data I was checking all Google to locate it สมัคร หวยบี
I am grateful for the clarity and insight your article has provided. Nhà cái sagaming
Amazing information you shared it is really appreciable thanks for sharing such great information. ยี่ กี
This is a good post. This post gives truly quality information. I really happy found this website eventually.
เดิมพันกีฬาออนไลน์
Your article has left a lasting impression on me, and I am grateful for the opportunity to learn from your work.
siêuno win
Thank you for sharing your knowledge and expertise with the world. game bài đổi thưởng uy tin
I was looking it for so long , and i found it finally that i know it will help me . 789bet คาสิโน
Great post. It was much needed. Love your simplistic style of explanation. snaptik tiktok downloader
BK8 không chỉ là một nhà cái, mà còn là biểu tượng của sự đổi mới và đẳng cấp trong ngành giải trí trực tuyến. Từ sản phẩm đa dạng, công nghệ tiên tiến, đến dịch vụ hỗ trợ tận tâm, BK8 đã chứng minh mình xứng đáng với sự tin tưởng của hàng triệu người chơi trên toàn thế giới. Hãy tham gia BK8 ngay hôm nay để trải nghiệm sự khác biệt và tận hưởng những giây phút giải trí tuyệt vời nhất!
This is a good post. This post gives truly quality information. I really happy found this website eventually.
123vip line
Players Run 3 will have to use their skills and agility to overcome obstacles and achieve high scores.
The depth of research and clarity of presentation in your writing are remarkable.หวย หุ้น เกาหลี ย้อน หลัง
That sounds like a fascinating experiment! If you’re ever looking for reliable data on different cases, you might find Arrest report lookup useful for accessing comprehensive details. Understanding various reports can be just as insightful as analyzing scientific results. Keep up the great work with your research!
Great post! Thank you for sharing informative post with us.
คาสิโนมือถือ
That’s a solid experiment with interesting insights into light intensity and photovoltaic efficiency! You might also find it useful to look into how geographical location affects solar energy performance—factors like sun exposure, elevation, and even property type can make a difference. If you’re ever researching property or land values for renewable energy projects in Florida, you can check out this helpful resource: Seminole County property records. Keep up the great experimentation!
This experiment is a great example of how hands-on activities enhance our understanding of solar energy and voltage variations. For those also interested in staying updated on public safety and legal developments, you can find detailed info on Missouri police activity here: https://missouri-arrests.org/. It’s always insightful to explore both scientific and societal trends together.
Good to become visiting your weblog again, it has been months for me. Nicely this article that i’ve been waited for so long. ติดต่อ 123betThanks for good sharing.
What a fantabulous post this has been. Never seen this kind of useful post. I am grateful to you and expect more number of posts like these. Thank you very much. mac-batteries.com
I admire this article for the well-researched content and excellent wording. I got so involved in this material that I couldn’t stop reading. I am impressed with your work and skill. Thank you so much. las-coloradas.com
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I have really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon! HINO TOTO
Great explanation! You’ve taken a topic that can be a little tricky and made it accessible. I feel much more confident about this now thanks to your post. ufabet vip
Pretty good post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I have really enjoyed reading your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you post again soon. Big thanks for the useful info. BOLAKAWAN
The tone throughout the article stayed professional but accessible, which made the content easier to connect with. ufabet ทางเข้า
That sounds like a fascinating experiment! For those interested in diving into related legal records involving environmental or energy projects, the Maine Court Records Database can provide useful insights into case filings and documentation. It’s always helpful to explore how scientific initiatives intersect with legal procedures.
Great breakdown of your solar energy experiment—it’s impressive how you’ve integrated physics concepts with practical observation. If you’re into daily mental challenges as much as scientific ones, this Wordle español online might be a fun addition to your routine. It’s a creative way to sharpen your language skills while keeping your mind active—much like experimenting with light and voltage!
We need to produce more for the Fnaf game so it’s more appealing and engaging.
I value the expertise and wisdom you bring to the table.
123bet สล็อต
I am inspired by your commitment to excellence and continuous improvement.
ag gaming
I am thankful to you for sharing this plethora of useful information. I found this resource utmost beneficial for me. Thanks a lot for hard work. lifestyleremedies.com
i was just browsing along and came upon your blog. just wanted to say good blog and this article really helped me. ARWANA 555
However, technology also offers solutions to pressing global issues, such as renewable energy and healthcare advancements palmettocleanenergy
I liked that you didn’t try to sound overly academic. Instead, you kept things professional but still easy to understand and connect with. ทางเข้า ufabet