Part of everyone’s daily routine involves the use of electricity; we use it so often that it is easily to forget how interesting and complex is the process that goes behind the generation of electricity. We have previously learned how a generator works, which basically produces electricity by rotating a magnet inside the a loop of copper wire; the change in the magnetic flux is what creates the electricity. Today, power plants keep using these methods to generate electricity; they rotate what known as the turbine which contains the magnets. What differences some power plants from others than is the process used to make that turbine turn. On this blog I will briefly talk about 3 types power plants: Coal-fired, Natural gas and Nuclear reactors.
In a coal- fired plant; coal, as you could’ve guess is raw material that is used to make the turbine rotate . This is how it works[1] :
-
The coal is pulverized into talcum powder; mixed with hot air and bowl in the firebox of the boiler.The coal/air mixture provides the most complete combustion and maximum heat possible
-
Highly purified water, pumped through pipes inside the boiler, is turned into steam by the heat. The steam reaches temperatures of up to 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit and pressures up to 3,500 pounds per square inch, and is piped to the turbine.
-
The enormous pressure of the steam pushing against a series of giant turbine blades turns the turbine shaft. The turbine shaft is connected to the shaft of the generator, where magnets spin within wire coils to produce electricity.
-
After doing its work in the turbine, the steam is drawn into a condenser, a large chamber in the basement of the power plant. In this important step, millions of gallons of cool water from a nearby source (such as a river or lake) are pumped through a network of tubes running through the condenser. The cool water in the tubes converts the steam back into water that can be used over and over again in the plant.
-
The cooling water is returned to its source without any contamination, and the steam water is returned to the boiler to repeat the cycle.
The following link will provide you a short animation of how all the steps from above are connected.coal_fired_animation
Because of the environmental impact , such as the gas emissions generated by coal-fired power plants, society have looked to to alternative ways of generating electricity. Among the new technological developments, natural gas power plants were created; they are the clean method for electricity generation.
Initially, wells are drilled into the ground to remove the natural gas. After the natural gas is extracted, it is treated at gas plants to remove impurities such as hydrogen sulfide, helium, carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons, and moisture. Pipelines then transport the natural gas from the gas plants to power plants. Power plants use several methods to convert gas to electricity[2]; The most basic natural gas-fired electric generation consists of a steam generation unit, where fossil fuels are burned in a boiler to heat water and produce steam that then turns a turbine to generate electricity[3]
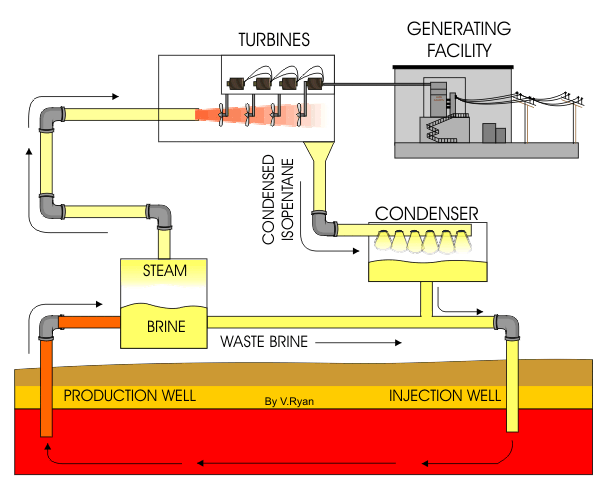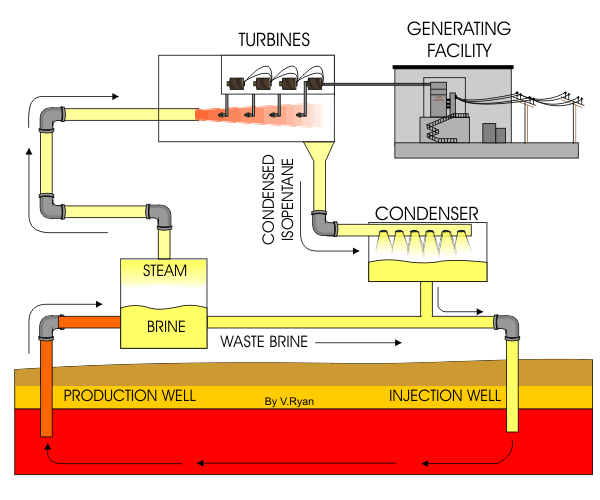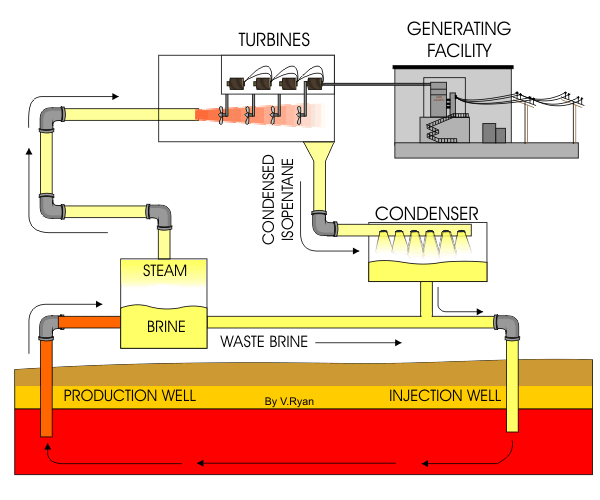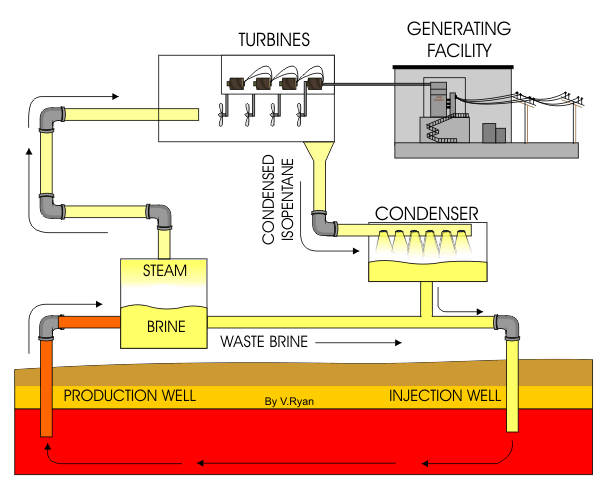
Figure 1 : Animation of cycle involved in a Natural Gas power plant
Finally, the last alternative power plant method is the nuclear reactor. This is without a doubt the most efficient method yet the most delicate and controversial. In general this kind of method generated high levels of heat that makes water to become steam which, consequently, drives the turbine and generates electricity . This is how it works :
In the reactor core the Uranium ( U-235 ) isotope fissions or splits, producing a lot of heat in a continuous process called a chain reaction. The process depends on the presence of a moderator such as water or graphite, to control this process. The moderator slows down the neutrons produced by fission of the uranium nuclei so that they go on to produce more fissions.The reactor core sits inside a steel pressure vessel, so that water around it remains liquid even at the operating temperature of over 320°C. Steam is formed either above the reactor core or in separate pressure vessels, and this drives the turbine to produce electricity. The steam is then condensed and the water recycled.[4]
There are two main designs for water reactor : Pressurized water reactor (PWR) or Boiling water reactor (BWR). The most popular is the PWR which has water in its primary cooling/heat transfer circuit and generated steam in a secondary chamber . The BWR is the least popular style; it creates steam in the primary circuit above the reactor. Below you can see an animation for both of this styles; notice how the BWR has one chamber less that the PWR structure:

Figure 2 : Animation of a PWR (Pressurized water reactor)

Figure 3 : Animation of a BWR (Boiling water reactor)
From these 3 methods it easy to guess that the cheapest method to generate electricity is the coal-fired method, and the most expensive and dangerous is the Nuclear reactor. But even though coal is the cheapest and responsible for provideo about 46 % of consumed electricity in the United states [1], it also is the dirtiest when it comes to air pollution [3]. Natural gas , on the other hand , is one of the leading clean energy sources for distributed generation[3]. While Nuclear energy supplies around 12 % of the world’s electricity [4] .
Sources :
[1] http://www.duke-energy.com/about-energy/generating-electricity/coal-fired-how.asp
[2] http://www.epa.gov/cleanenergy/energy-and-you/affect/natural-gas.html
[3] http://naturalgas.org/overview/uses-electrical/
[4]http://www.world-nuclear.org/nuclear-basics/how-does-a-nuclear-reactor-make-electricity-/
