STIRLING MOTOR
HISTORY & DEVELOPMENT
The Scottish religious Robert Stirling (1790-1878), invented this engine in 1816. Another important contribution in the development of the automotive machine handed the French genius Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), who was the first scientist to make a theoretical interpretation of the operation of heat engines, establishing the physical principles involved in their movement. This theory allowed us to understand more clearly the phenomenon that allows the Stirling produce motive force.
Originally conceived in 1816, was created by Robert Stirling as the first engine designed to rival the steam engine, due to high efficiency, if it is compared with steam engines, besides its easy to be applied to any source heat. That’s until the electric and internal combustion engines replaced Both at the turn of the 20th century. Stirling engines have only been used in very Specialized applications ever since, for example, in the 1960’s a tiny Stirling engine was developed to power an artificial heart and today They are Commonly used To provide the cooling for infrared guidance systems in missiles. However, With the Increased focus on Environmental Concerns and our quest for cleaner, more efficient power sources, the Stirling engine is back in the spotlight as a feasible power source for wide-scale use.
HOW IT WORK’S
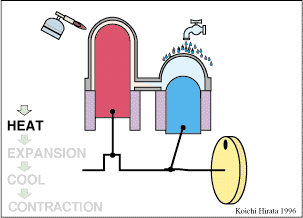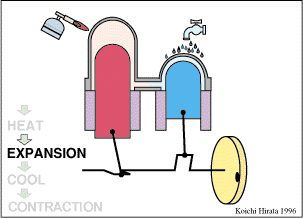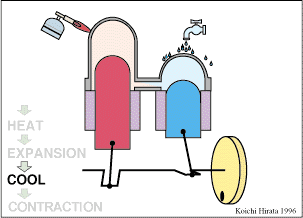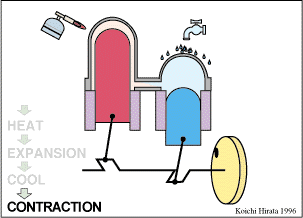
The hot air Stirling engine uses a fixed heat source for heating air in your cylinder. It can be considered external combustion, as it requires no burn fuel therein and to operate, does not transfer heat to the environment. It’s movement is due to differences in air pressure between the warmer and cooler portion. The central mechanism of a Stirling consists of two pistons / cylinders, one for dissipating heat and displace warm air into the cold section (vice versa). In practice this cylinder functions as heat exchanger and is called regenerator. The other piston delivers power to apply torque to the crankshaft.
Every Stirling engine has a sealed cylinder with one part hot and the other cold. The working gas inside the engine (which is often air, helium, or hydrogen) is moved by a mechanism from the hot side to the cold side. When the gas is on the hot side it expands and pushes up on a piston. When it moves back to the cold side it contracts. The two piston type Stirling engine has two power pistons. The displacer type Stirling engine has one power piston and a displacer piston.
Displacer Type:
The displacer type Stirling engine is shown here. The space below the displacer piston is continuously heated by a heat source. The space above the displacer piston is continuously cooled. The displacer piston moves the air (displaces the air) from the hot side to the cold side. When the engine pressure reaches its maximum because of the motion of the
displacer, a power piston is pushed by the expanding gas adding energy to the crankshaft.

Two Piston Type:
The two piston type Stirling engine is shown here. The space above the hot piston is continuously heated by a heat source. The space above the cold piston is continuously cooled. But its during the expansion part of the cycle where the engine gets its power.
MODERN DAY USES
Military uses:
A Swedish army submarine is Equipped with Stirling engines for its auxiliary electrical production in order to Provide the vital functions in the event of unavailability of the main source. Its silence of operation is a major asset In this application. In the same context, the Australian navy ADOPTED Also have it for a 3000 tons displacement submarine.
Spatial domain:
Some satellites get energy through a Stirling engine. The efficiency is high Particularly Considering the great Differences in temperature. The hot source Consists of radioactive isotopes. The use of radioactive elements is not very ecological, it presents Risks at the time of the take-off of the rocket. The justification comes owe owing to the fact That solar panels can be dirtied or be destroyed in Un certain zones of space, as near Mars.
Domestic uses:
Small installations were developed in order to function in cogeneration: electricity supply and dwelling heating. One chooses fuel (oil, wood, wood pellets…) to make electricity and to heat a house. During certain periods, it is possible to sell excess electricity if one is connected to the grid.
Some pleasure boats are equipped like that.
Generators :
After the second world war, Philips developed and marketed the generator which group had a power of approximately 150 Watts.
Cryogénic domain :
The reversibility of the Stirling engine is used in order to produce cold in an industrial way. Its efficiency is then excellent. In this type of operation, described on this site in the page “Stirling coolers”, we provide mechanical energy to the engine. In fact, we transfer calories from the cold source the hot source, like in a domestic refrigerator. This mode of operation is so efficient that we use this type of installation to liquefy certain gas.
-Paradox : use sun for generating electricity by a Stirling engine, then this electricity drives a Stirling engine for making cold. How to make ice under a blazing sun, and all thanks to him!!
-At last i would like to show you this 10 top modern uses of a stearling motor as a curiosity, which i found to be pretty interesting:
Picture gotten from —> http://www.discoverthis.com/article-stirling-engine-top10.html
WHAT’S FOR THE FUTURE?
A very promising use of Stirling engines is cogeneration, where they produce both heat and electricity for homes. If the excess heat produced by Stirling engines was directly used to replace furnaces and water heaters in homes, this would yield a dramatic increase in energy efficiency. This is especially useful for “off-grid” applications where people are too far from power plants to get electricity over cables. Many companies are currently looking into using Stirling engines to replace the current systems in refrigerators. Driven in reverse, Stirling machine pistons manipulate the contained gas to affect temperatures outside the machine. Stirling engines would use as much as 50% less electricity and even more importantly, they do not require CFCs for cooling. One company, Global Cooling, has developed a solar-powered Stirling refrigerator that could be used in the developing world for keeping food and medicine cool.
Researchers at Los Alamos are currently working to design a Stirling engine that would cool the gas so that it becomes a liquid, which would make it much easier to transport in conventional pipelines.Their new engine uses intense acoustic energy instead of pistons for the heat transfer. Constructed of welded pipes, the engine is remarkably simple, efficient, and inexpensive.
Perhaps the greatest challenge facing Stirling engines is the popularity of internal combustion engines. Designers of Stirling engines will need to offer incredible advantages to be able to attract manufacturers aways from gasoline engines. In addition, new materials need to be developed for the hot parts of the engine; this is the part that is most likely to wear out. Once they are mass produced, the cost of Stirling engines will come down greatly and their popularity should increase.
PELTIER DEVICE
PELTIER HISTORY
Early 19th century scientists, Thomas Seebeck and Jean Peltier, first discovered the phenomena that are the basis for today’s thermoelectric industry :
-Seebeck found that if you placed a temperature gradient across the junctions of two dissimilar conductors, electrical current would flow.
-Peltier, on the other hand, learned that passing current through two dissimilar electrical conductors, caused heat to be either emitted or absorbed at the junction of the materials.
It was only after mid-20th Century advancements in semiconductor technology, however, that practical applications for thermoelectric devices became feasible. With modern techniques, we can now produce thermoelectric “modules” that deliver efficient solid state heat-pumping for both cooling and heating; many of these units can also be used to generate DC power at reduced efficiency. New and often elegant uses for thermoelectrics continue to be developed each day.
PELTIER STRUCTURE
Looking at the figure, we can see that practically two semiconductor materials, include one with and one with N channel P channel, linked together by a copper foil.
If in the N side of the material feeding the positive polarity on the side of the material P the negative polarity is applied, the copper plate cools the top while the bottom heat.
If in the same cell, the power supply polarity is reversed, that is, applied on the side of the material N negative polarity and on the side of P positive material function heating / cooling is reversed top heated and the lower cooling. It is, therefore, static heat pump that requires neither gas nor moving parts. Physically a Peltier element module 1 mm cubic blocks are connected electrically in series and thermally in parallel.Today, they are solidly constructed and have the size of a quater. Semiconductors are made for Tellurium and Bismuth type P or N (good conductors of electricity and heat) which facilitate the transfer of heat from cold to hot by the effect of a direct current side.
PELTIER THEORY
When DC voltage is applied to the module, the positive and negative charge carriers in the pellet array absorb heat energy from one substrate surface and release it to the substrate at the opposite side. The surface where heat energy is absorbed becomes cold; the opposite surface where heat energy is released, becomes hot. Reversing the polarity will result in reversed hot and cold sides.
CURRENT DAY USES OF THE PEILTER DEVICE
-Currently, one of its most common uses is as part of the CPU cooling computers.
-Board control Refrigerator: the Peltier module for cooling booths telecommunications network and dashboards within the factories are used.
–Small sump constant temperature: In the experiments of culturing microorganisms is required to control the temperature near the body temperature and the ambient temperature. The precise temperature control near ambient temperature with cold hampers or heating facilities, the best thing is the Peltier module.
-Milk cooling: Recently established machines coffee and soft drinks are, with increasing free sites beverage services in different types of restaurants. This machine coffee service has put a milk cooler wearing a Peltier module. It may take 2-4 packs of 1 liter milk and keep it cold.
-In the field of air conditioning there are air conditioning equipment that control temperature and humidity equipped with compression refrigerators which use refrigerant fluids based on compounds of fluorine and chlorine in greater or lesser extent that attack the ozone layer.
-They have also developed air dehumidification equipment employing chemical absorbers and compression equipment generally of large dehumidifier power.The presented technology involves passing aire from a room , residence, etc.., Drawn by a fan through some cold packs, which are cooled by Peltier effect, collecting the condensed water in the system at a lower tray. It is very suitable for controlling moisture in humid climates, which eliminate noise and vibration, avoiding the moving parts of the compressor that carry current dehumidifiers and refrigerants, as potential environmental contamination compact
Problems related to Peltier cooling
-The power usage and high power dissipation are the biggest problems related to peltier cooling. In the days of first-generation Pentium CPUs, readymade peltier/heatsink combinations were widely available, which could be installed and used just like a regular heatsink. For today’s CPUs having a power dissipation of over 100W, building a Peltier CPU cooler using just a peltier element and a heatsink is quite a challenge, and ready-made peltier coolers are scarce and expensive. With such coolers, over 200W of heat may be dissipated inside the case. The resulting cooling system will be expensive to run, due to its high power usage, and not very eco-friendly. The large power dissipation will require powerful (and thus loud) fans.
-Also, keep in mind that if the cooling of the peltier element fails (e.g. fan failure or pump failure in case of watercooling), the results will be more disasterous that if a conventional cooling system fails. Even if your CPU has a thermal protection that will cause it to shut down if the temperature gets too high, the peltier element may still kill it by continueing to heat it up long after it has shut itself down.
-Another problem related to peltier cooling is condensation. Since it is possible to cool components below ambient temperature using peltier elements, condensation may occur, which is something you’ll definitely want to avoid – water and electronics don’t mix well. The exact temperature at which condensation occurs depends on ambient temperature and on air humidity
Advantages of Peltier elements
-After having focused on problems related to Peltier cooling, let’s not forget about their biggest advantage: They allow cooling below ambient temperature, but unlike other cooling systems that allow this (vapor phase refrigeration), they are less expensive and more compact.Peltier elements are solid-state devices with no moving parts; they are extremely reliable and do not require any maintainance.
—-SOURCES—
www.stirlingengine.com
en.wikipedia.org
www.stirlingshop.com
www.heatsink-guide.com



Great post, you have pointed out some fantastic points , I likewise think this s a very wonderful website