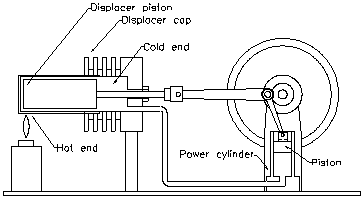
Solar energy is defined as a “radiant light and heat from the sun”, it is channeled using a “range of ever-evolving technologies” for example solar heating, solar photovoltaic, solar thermal electricity, solar architecture and artificial photosynthesis. There are two types of solar energy: passive solar and active solar. It depends on the procedure of how they capture, convert and distribute solar energy. They also have different use in the solar energy. The passive solar energy orientates the buildings to the Sun and selects materials with “favorable thermal mass or light dispersing properties”, it also designs spaces that naturally circulates air. The active solar energy used the photovoltaic panels and solar thermal collectors to harness the energy.
The technology for solar energy uses the sun’s energy and light to provide light, heat, electricity, hot water and also cooling for homes, businesses and industry.
President Obama announced that they are trying to build more support for the impact of global warming on our world. This is part of s broader campaign to build public support for an Environmental Protection Agency that will limit carbon pollution from coal-fired power plants and “is expected to create a major new market for zero-carbon carbon energy from sources same as wind and solar.”
All the effects that the world population has made over our planet regarding climate change are felt in all the corners of the world. The water is growing faster in dry regions, torrential rains increasing in wet regions, heat waves are becoming more common and much more severe. The wildfires are growing worst and the forests are dying under the assault from heat loving insects. “The White house,[…], wants to maximize its impact to drum up a sense of urgency among Americans about climate change – and thus to build political support for contentious new climate change regulation that President Obama plans to issue in June.”
“Today’s commercial solar cells”, most of the time made from silicon, convert sunlight into electricity with an efficiency of only 10% – 20%. Modules of today’s cells, “incorporated in the power grid” produces electricity. “Current standard cells have a theoretical maximum efficiency o 31 percent because of the electronic properties of the silicon material. New materials that are arranges in “novel ways’, can “evade that limit”, with some multilayer cells “reaching 34% efficiency”. Another idea that scientists have thought about to enhance efficiency involves the development in nanotechnology, the engineering of structures on sizes comparable to those of atoms and molecules, measured in nanometers”.
Sources
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_energy
http://www.nytimes.com/2014/05/09/us/politics/obama-to-give-push-on-climate.html?_r=0
http://www.engineeringchallenges.org/cms/8996/9082.aspx