Some people think that all it takes to generate power is flipping a switch! No it is not that simple. Mother nature provided us with different sources that we can use to generate electricity, some of those sources are limitless such as wind or solar power. On the other hand our generation mostly depend on thermal power plants such as coal, natural gas, and nuclear plants to generate power. For every energy source a chemical or mechanical process is required to turn it into usable electricity. Researchers work everyday to find innovative ways to generate power, and convert natural sources into usable energy through different methods.

Coal and Natural Gas:
Fuels like Coals, natural gas are used to heat water until it produces steam. Steam used in the process to power the turbine which generates electricity. Steam turns the blades around a router inside of a turbine which is connected to a main shaft which spins magnets with coals inside of generators. The generator inside of the turbine converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Steam is an efficient method of producing energy since the water used in the process can be recycled and reused. Old coal power plants, are significantly less efficient and produces higher levels of waste heat. Studies show that 40% of the world’s electricity comes from coal. Natural gas is much more cleaner choice for thermal power generation. Natural gas can lower CO2 emissions by up to 60 percent. The US have more natural gas reserved than any other country. A natural gas facility is less expensive to build that as of a coal facility, and at least a fourth as expensive as nuclear power plant.
Nuclear Plants:
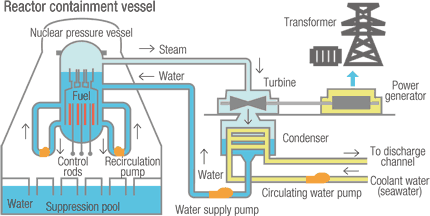
There is not a lot of big differences between generating electricity using nuclear power plants and fossil-fuel plants. The only difference is that in nuclear power plants they use the steam that’s been heated through atomic fission rather than burning coal, or gas. Nuclear plants don’t use a lot of fuel which is a great advantage, unlike coal which needs to be refueled regularly. However waste water is much more hotter than that of fossil plants, that is why large cooling towers are attached to solve this problem. There are many reasons that made nuclear power plants are less attractive, such as disposing the contaminated accessories from the fuel cores. As well as the accidents that could lead to a disaster like what happened at the Three Mile Island back in 1979.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_UwexvaCMWA
References:
http://americanhistory.si.edu/powering/generate/gnmain.htm
http://www.ntpc.co.in/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=56&Itemid=66&lang=en
http://www.powerscorecard.org/tech_detail.cfm?resource_id=6


I definitely see your point that the energy debate can be oversimplified. Many want a direct answer, but as you imply with your blog post, we need to have a wide range of options available to fuel our economy.
Looking at the three you posted, I would definitely back more nuclear power in the US. While there are safety concerns, the class text underscores the point that Western plants are much more safe than any nuclear facility built in Russia or parts of Asia. Furthermore, deploying more nuclear energy will allow us to cut our carbon emissions while continuing to build our understanding of renewable sources such as wind and solar.
Mohammed,
I like the way you compared each three of the energy sources. It was very easy to understand by your explanations and your diagrams were great along side your explanations.
I agree with you that we need to have a wide range of fuel options. Unfortunately, as you said, many people don’t know how energy generation works – they just flick the switch and their lights turn on. Knowing how these resources work and how energy is produced is important, especially how it benefits or may be harmful to our environment.