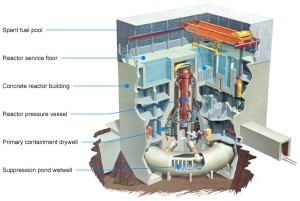
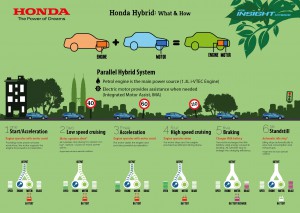
A group of friends and I went to the museum of science last week to explore the exhibits on conservation at home, investigate, energize, and many others. Our group took our time by walking to the science museum because it was a lovely spring afternoon. On the way there we saw robins and geese by the esplanade as we talked about our last times visiting the science museum. The first exhibit we went to was the conserve at home with a massive model house you can explore and walk through. When you first walk in there is a meter reader that was unfortunately not working. The meter has a metal disk that rotates as power is consumed tracking the results. Near the meter was the “Energy Audit” station. This allowed you to detect thermal defects and air leakages and what materials were most effective for retaining heat. This process is done by recording the temperature variations of the homes outer surface, white for warm regions and black for cool. The viewer moved blocks upon the roof of the house to see which materials saved heat and what ones didn’t. The group stayed and watched a few seconds of the “Neighborhood Energy Stories” before we moved on to “Get Energy Efficient” with blocks. It was really interesting because the viewer would place a block onto a scanner and information about the topic would show up on a computer screen. I found the facts about automobiles the most relevant because we have discussed it multiple times in class. Their facts are a little out dates but they said “Buy a car that gets 30.7 mpg to save up to 13.5%.If you drive 15,000 miles in a year, this could mean a savings of $1,000 each year in fuel”. With Obama’s action plan in place that by 2025 cars will have to have the mileage of 54.5 mpg which will save even more money. The next section about recycling I found truly fascinating because it showed
first exhibit we went to was the conserve at home with a massive model house you can explore and walk through. When you first walk in there is a meter reader that was unfortunately not working. The meter has a metal disk that rotates as power is consumed tracking the results. Near the meter was the “Energy Audit” station. This allowed you to detect thermal defects and air leakages and what materials were most effective for retaining heat. This process is done by recording the temperature variations of the homes outer surface, white for warm regions and black for cool. The viewer moved blocks upon the roof of the house to see which materials saved heat and what ones didn’t. The group stayed and watched a few seconds of the “Neighborhood Energy Stories” before we moved on to “Get Energy Efficient” with blocks. It was really interesting because the viewer would place a block onto a scanner and information about the topic would show up on a computer screen. I found the facts about automobiles the most relevant because we have discussed it multiple times in class. Their facts are a little out dates but they said “Buy a car that gets 30.7 mpg to save up to 13.5%.If you drive 15,000 miles in a year, this could mean a savings of $1,000 each year in fuel”. With Obama’s action plan in place that by 2025 cars will have to have the mileage of 54.5 mpg which will save even more money. The next section about recycling I found truly fascinating because it showed  examples people could see and interact with. In a see-through panel the science museum displayed a 100 plastic bags so children can visualize just how much waste they create within a year. Broken glass and bottles can become works of art within the home as floor tiles. Plastic bottles and milk gallons become sturdy and long lasting Adirondack lounge chairs that can last outdoors. One of our group’s favorite exhibit was the “Turn Your Energy into Light” exhibit. There were three light bulbs set up (LED, Incandescent, and CFL) in which the viewer spun a wheel to see which light bulb uses the least amount of energy. CFLs are the better bulbs out of the three because they are four times more efficient than incandescent bulbs and can last up to 15,000 hours. Scientists believed in the next few years LED bulbs would beat CFLs in the market, which happened in 2011 when LEDs were proven to last 25,000 hours.
examples people could see and interact with. In a see-through panel the science museum displayed a 100 plastic bags so children can visualize just how much waste they create within a year. Broken glass and bottles can become works of art within the home as floor tiles. Plastic bottles and milk gallons become sturdy and long lasting Adirondack lounge chairs that can last outdoors. One of our group’s favorite exhibit was the “Turn Your Energy into Light” exhibit. There were three light bulbs set up (LED, Incandescent, and CFL) in which the viewer spun a wheel to see which light bulb uses the least amount of energy. CFLs are the better bulbs out of the three because they are four times more efficient than incandescent bulbs and can last up to 15,000 hours. Scientists believed in the next few years LED bulbs would beat CFLs in the market, which happened in 2011 when LEDs were proven to last 25,000 hours.
After completing our walk through “Conservation at Home” exhibit the group toured an exhibit called “Investigate”. The group’s attention was grabbed in the bathroom where two sinks were used to discover if water drains in the same direction on different hemispheres. The answer is that it  doesn’t matter where on Earth you are the water drainage is random and proven a myth. Next to the sinks was a display of how a toilet works which can come in handy for any homeowner or apartment renter. I wish it explained more about how to maintain a toilet and keep a sink from clogging. Along the way there were farmhand tools, Archimedes screw, and scientist stories.
doesn’t matter where on Earth you are the water drainage is random and proven a myth. Next to the sinks was a display of how a toilet works which can come in handy for any homeowner or apartment renter. I wish it explained more about how to maintain a toilet and keep a sink from clogging. Along the way there were farmhand tools, Archimedes screw, and scientist stories.
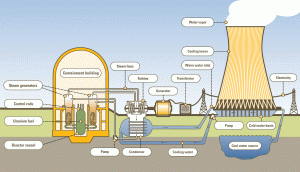
“Energized” is what we were after visiting the exhibit on solar, wind, and hydro energy in Massachusetts. It is estimated that by 2020 22% of Massachusetts electricity will come from renewable sources. I love wind turbines so much because the first turbine to be installed in Massachusetts was in Jiminy Peak in Hancock Ma which I can see from my home window! As well as oddly enough near my hometown will be the largest solar power plant in New England (Pittsfield, Ma). Have driven by it myself I can tell you it is pretty spectacular to see over 6,000 solar panels in the same spot that used to be toxic waste. The town of Harvard has the most solar panel installations with 21 installed and 75 in planning stages. The group did not get a chance to tour the wind turbines on the roof of the science museum but will have to check it out at a later date.
The museum of science is overall a wonderful place for people of all ages to learn and interact with  science but especially children. The way the exhibits are created offer interactive learning for children which helps them remember what they saw in a fun and non-threatening way. I believe all teachers, professors, and parents should bring their children to science museums especially when they have special exhibits. I found the exhibits outside of what was required within class the most intriguing. I found them more intriguing because a lot of what we have researched and discussed within class is at the museum and it was repeated while the other exhibits were not. I did love how interactive everything was which made individuals understand and visualize the information better than within class.
science but especially children. The way the exhibits are created offer interactive learning for children which helps them remember what they saw in a fun and non-threatening way. I believe all teachers, professors, and parents should bring their children to science museums especially when they have special exhibits. I found the exhibits outside of what was required within class the most intriguing. I found them more intriguing because a lot of what we have researched and discussed within class is at the museum and it was repeated while the other exhibits were not. I did love how interactive everything was which made individuals understand and visualize the information better than within class.