Nikola Tesla (1896)
Nikola Tesla is an engineer and physicist born in Croatia on July 10 of 1856. Tesla moved to America, New York, in 1884 where he was hired as an engineer to work for Thomas Edison at Thomas Edison’s Manhattan headquarters, where he worked for about a year impressing Edison with his cleverness while making notorious improvements to Edison’s inventions. Nevertheless, after a few months working together, Edison and Tesla started to have scientific conflicts which ended their relationship. After several failed attempts his life changed when he developed an alternating current (AC) system and funded his new Tesla Electric Company where he had successfully filed several patents for AC- based inventions.

Over time, his inventions caught the attention of George Westinghouse, and American engineer and businessman who had been looking for a solution to supply the nation with long distance power. In 1888, Westinghouse purchased Tesla patents becoming a direct competition to Thomas Edison.
In 1890’s Tesla created the “tesla coil” today best defined by the dictionary as “a form of the induction coil for producing high-frequency alternating currents” but in reality, it is a creation by Tesla in his search for wireless electricity. This image below shows in a series of simple steps how this system works

How does it work?
- The transformer boost the voltage
- The power source is hooked up to the primary coil. The primary coil’s capacitator acts like a sponge and soaks up the charge.
- Electric current builds up in the capacitor until it reaches a tipping point. The current streams out of the capacitor into the coil. Once the first capacitor is completely wrung out and has no energy left the inductor reaches its maximum charge and sends the voltage into the spark gap.
- The huge voltage current flows through the spark gap into the secondary coil. The energy sloshes back and forth between the two coils.
- The secondary coil has a top- load capacitor that concentrates all the current and can eventually shoot out lighting like bolts. (Information by live science)
In addition to all his creations, in 1895 “Tesla designed what was among the first AC hydroelectric power plants in the United States, at Niagara Falls. The following year, it was used to power the city of Buffalo, New York, a feat that was highly publicized throughout the world.”
Current work and technology in this area


One of the newest technologies in this area in the Tesla Electric Car, This car claims to be zero emissions and zero compromises utilizing an advanced electric powertrain that delivers “exhilarating performance” The tesla website describes this technology consist of “ only one moving a piece: the rotor. As a result, acceleration is instantaneous, silent and smooth. Step on the accelerator and in as little as 2.8 seconds Model S is traveling 60 miles per hour, without hesitation, and without a drop of gasoline. Model S is an evolution automobile engineering”
-Consist of two (2) motors one in the front and one in the rear
-This car uses a three-phase alternating current (AC) induction motor.
-The motor has two primary components a rotor, which is a shaft of steel with copper bars running through it. The stator surrounds but does not touch the rotor. The stator has two functions: it creates a rotating magnetic field and it induces a current in the rotor.
– A touch screen controls most of the car’s functions
In addition, to all this wonderful creation, the fact that this car is chargeable is not a disadvantage. Tesla has created a wide range of supercharging stations. “The word’s fastest charging station” which are free connectors that charge the tesla car in minutes instead of hours. Yes, the process last longer that a gas station but this stations are strategically placed to minimized stops during long distance travels conveniently located along the road.
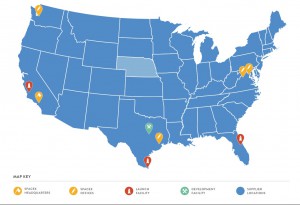
Today we count with 597 supercharger station with 3,481 superchargers. The picture below shows with red dots supercharger locations on the map.

References:
http://www.biography.com/people/nikola-tesla-9504443
http://www.history.com/topics/inventions/nikola-tesla
http://www.livescience.com/46745-how-tesla-coil-works.html
https://www.teslamotors.com/supercharger