Solar power has grown exponentially in the last years, driven largely by the need to develop and meet the challenges of energy generation.
This growth has occurred through different mechanisms that have been building out in different countries, which have increased the overall capacity of manufacturing, distribution and installation of this technology.
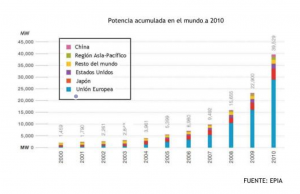
At the end of 2010, the accumulated power in the world, according to the European Photovoltaic Industry Association (EPIA), was 40,000 MVp, of which nearly 29,000 MVp focused on the European Union.
In the graph below we can see the historical representation of the global MV and the great growth that has been experienced. The three areas with higher global interest in this source are: Europe (most notably Germany and Spain with more than 52% of the world total), Japan and USA.
As we can see, the largest increase took place in 2010, which over the previous year, represented a growth of 72%.
–Germany
It is one of the world leaders in the installation of this type of energy, largely because legislation promotes and contributes to the installation and use of renewable energy (“German Renewable Energy Act”). In 2011 were installed near 7.5 GW, which produced 3% of the energy consumed in the country.
It is very common to find this kind of energy in domestic houses, residents pay a small tax that allows defray in
–Japan
This country is characterized by its rapid expansion since 1990, getting to be a world leader in the manufacture of photovoltaic modules, and is among the top 5 in terms of installation.
–EEUU
Since 2010 is one of the largest photovoltaic markets activity, and has numerous plants, including the largest plant in the world dedicated exclusively to this kind of energy.
Although USA doesn’t keep a fair policy in all states, have been setting many goals independently as to renewable energy is concerned, allowing a globally growth.
Many homes enjoy their own solar panel, especially in California, built during the “Million Solar Roof” initiative.
The main challenge being pursued is to innovate facilities to become energy directly plug (plug-and-play), ie, make it as accessible and simple as accessing the network.
Sources:
http://www.energia-solar.org.es/m-energia-solar-usa.html
http://www.censolar.es/menu2.htm
http://web-japan.org/niponica/pdf/07/Niponica_07_digest_Spa.pdf
http://www.csd.ca.gov/Portals/0/Documents/FinalSpanish.pdf