Electricity can be obtained in many ways. I’ll explain three different sources: coal, natural gas and nuclear power, and how this plants transform those sources in energy.
-Coal
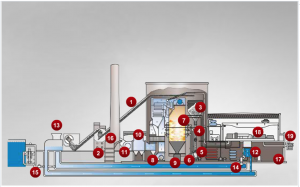
An electricity generation plant is a station that produces energy from a particular material and a technology used, such as in this case coal.
In the following link we can see a video that shows the process this material passes to be converted into energy:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e_CcrgKLyzc
As we see, the coal is stored in a location near the central park and is driven by a conveyor to a hopper where it is sprayed. Later it is injected into a boiler and is mixed with hot air to be burned; thus the steam is obtained, and this one drives the turbines and makes the electric motor moves, converting mechanical energy into electricity.
The steam used in the previous process becomes liquid by a condenser which acts with cold water from the sea or river.
–Nuclear power
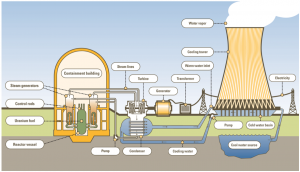
A nuclear power plant uses the heat that is obtained by the fission of uranium nuclei to produce electricity installation. This heat, as in the previous station, is used to generate steam which drives the turbine or generator and power is obtained.
The most characteristic part of a nuclear plant is the containment building, usually composed of a cylindrical base and finished in a dome shape. In this part we can find the main components are the reactor, pressurizer, and coolant pumps.
Once the heat is generated by the fission of the nuclei in the reactor, is transmitted to the refrigerant being liquid and is conducted to the steam generators, where through different pipes get the turbine and is converted into electricity with the help of an electric generator.
-Natural gas
Natural gas is a combustible gas that is located in nature, in underground reservoirs in porous rocks, and is a mixture of hydrocarbons (mainly methane). It is the most used energy source after oil and coal.
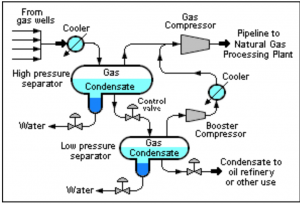
The process can be divided into the following stages: separation, dehydration, refrigeration of gas and liquids and distillation.
Natural gas processing consists of separating all of the various hydrocarbons and fluids from the pure natural gas, to produce what is known as ‘pipeline quality’ dry natural gas. Associated hydrocarbons, known as ‘natural gas liquids’ (NGLs) can be very valuable by-products of natural gas processing. NGLs include ethane, propane, butane, iso-butane, and natural gasoline. The actual practice of processing natural gas to pipeline dry gas quality levels can be quite complex, but usually involves four main processes to remove the various impurities:
1.Oil and Condensate Removal
2.Water Removal
3.Separation of Natural Gas Liquids
4.Sulfur and Carbon Dioxide Removal
Sources:
https://primis.phmsa.dot.gov/comm/FactSheets/FSNaturalGasProcessingPlants.htm
http://www.mobilindustrial.com/ind/spanish/yourindustry_energy_coal.aspx
http://comunidad.eduambiental.org/file.php/1/curso/contenidos/docpdf/capitulo16.pdf