On 11th March 2011 happened one of the most serious nuclear accident in history after the one occurred in Chernobyl.
One the most violent earthquake recorded and one tsunami off the coast of Japan seriously affected the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant.
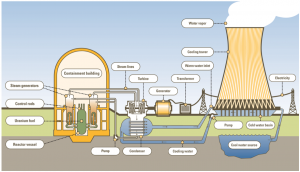
At the moment of the accident there were a total of 6 reactors available, three of them were in operation; immediately after the earthquake they stopped automatically, however, electrical energy was needed to cool them, but the supply of electricity stopped because of the earthquake, so diesel engines were used, but with the subsequent arrival of the tsunami also stopped working. At this time the problems started: unable to cool down, the meltdown of the reactors was confirmed.
The day after the earthquake, there were several explosions that led to the evacuation of the population within first 20 kilometers and 40 kilometers later, since it was an accident classified Level 7 of INES (radioactivity were released to the exterior).
Fukushima marked a before and after in the development of nuclear energy.
–Japan’s new energy strategies:
Ambitious Targets Toward 2030:
-Halving CO2 emissions from the residential sector.
-Maintaining and enhancing energy efficiency in the industrial
sector at the highest levels in the world.
-Maintaining or obtaining major shares of global markets for
energy-related products and systems.
+Domestic energy-related CO2 emissions will decline by 30% or
more in 2030
—Securing resources and enhancing supply stability
—An independent and environment-friendly energy supply
structure
—Realizing a low carbon energy demand structure
—Building next-generation energy and social systems
—Developing and disseminating innovative energy technologies
You can see a really clear information about the Specific Measures to Achieve Targets of Japan in the below link (second point):
http://www.jetro.go.jp/mexico/topics/20100708514-topics/01_ANRE_METI.pdf
Sources:
http://energia-nuclear.net/accidentes-nucleares/fukushima.html
http://www.izt.uam.mx/newpage/contactos/anterior/n80ne/fukushima.pdf
http://www.jetro.go.jp/mexico/topics/20100708514-topics/01_ANRE_METI.pdf