Going to the Museum of Science with the class was pretty exciting because even though I live in the area, I never get to go enjoy the museums in Boston as much as I would like. I learned quite a lot and took a lot of pictures while at the museum. The first exhibit I visited was Catching the Wind. It was all about wind powered energy and wind turbines. Wind power is a natural and clean resource generated by wind turbines to perform tasks or convert wind into usable electricity. When sunlight hits the earth and hits the air unevenly, the temperature difference starts moving the air, as warmer air rises and cooler air moves in to take its place, creating wind. Wind turbines catch the energy of the wind and change it into a form we can use. As the wind turns a turbines blades, the machinery inside the nacelle converts the energy into electricity. The first Windmill to generate electricity was built in 1888 in Cleveland, Ohio by Charles F. Brush and it generated up to 12 kilowatts of electricity.
The parts of a turbine include:
- Blades- airfoil-shaped wings that are moved by the wind.
- Tower- holds the blades up high where the wind is steady.
- Nacelle- holds the turbine’s machinery on top of the tower. The nacelle sits on yaw motors that turn the turbine to face into the wind.
- Hub(Nose Cone)- center where the blades connect with the low-speed shaft. The blades, hub, and low-speed shaft all turn as one piece.
- Low-Speed Shaft- strong, heavy shaft that supports the weight of the blades and connects to the gearbox.
- Gearbox- a group of gears that uses the slow rotation of the low-speed shaft to help speed up the rotation of the high-speed shaft.
- High-Speed Shaft- Spins faster than the low-speed shaft, enough to generate electricity in the generator. A brake stops the shaft when the wind is too strong, protecting it from damage.
- Electric Generator- produces electricity when the high-speed shaft spins a magnet inside it. The electricity can either be added to the electric grid or stored in batteries.
- Yaw Motors- turn the turbine to face into the wind
- Electronic Controller- a computer that allows the turbine to function without an operator on-site. The controller has many tasks: monitoring the amount of electricity generated, controlling the yaw motors, and adjusting the blade angle.
- Anemometers and Wind Vane- sit on top of the nacelle, measuring wind speed and direction. This information is transmitted to the electronic controller to keep the turbine functioning optimally.
The decision to install a wind turbine is generally based on a location’s wind speed and duration over the course of a year. Other factors considered before installing wind turbines include:
- how much electricity a wind turbine is capable of generating
- a wind turbine’s efficiency
- the cost of the turbine
- the time it will take for the turbine to return a profit
- how wildlife populations will be affected
- acceptance by the community

The next exhibit I visited was Energized! This exhibit was all about energy we use today and solar energy. We use energy every day as electricity for our appliances or fuel for our cars. The amount of energy we use every day continues to increase . The fossil fuels we currently rely on-including petroleum, coal, and natural gas- are damaging the environment. This is why renewable energy is so important. It helps to balance our needs for energy and cleans the environment. These renewable energy sources are found all around us. Such as the motion of wind and water, the light and heat of the sun, and in the heat underground.
Solar panels, also called photovoltaic panels, transform sunlight into electricity. When the sun’s radiation hits the panel, electrons get energized and start to move. Flowing electrons create an electrical current which we call electricity. The angle at which sunlight hits solar panels makes a big difference in how much electricity is generated. Some installations have motors that move the panels throughout the day so the sun always shines directly on them. The potential of solar energy is that wherever there is sunshine, solar energy can be harnessed to generate electricity.
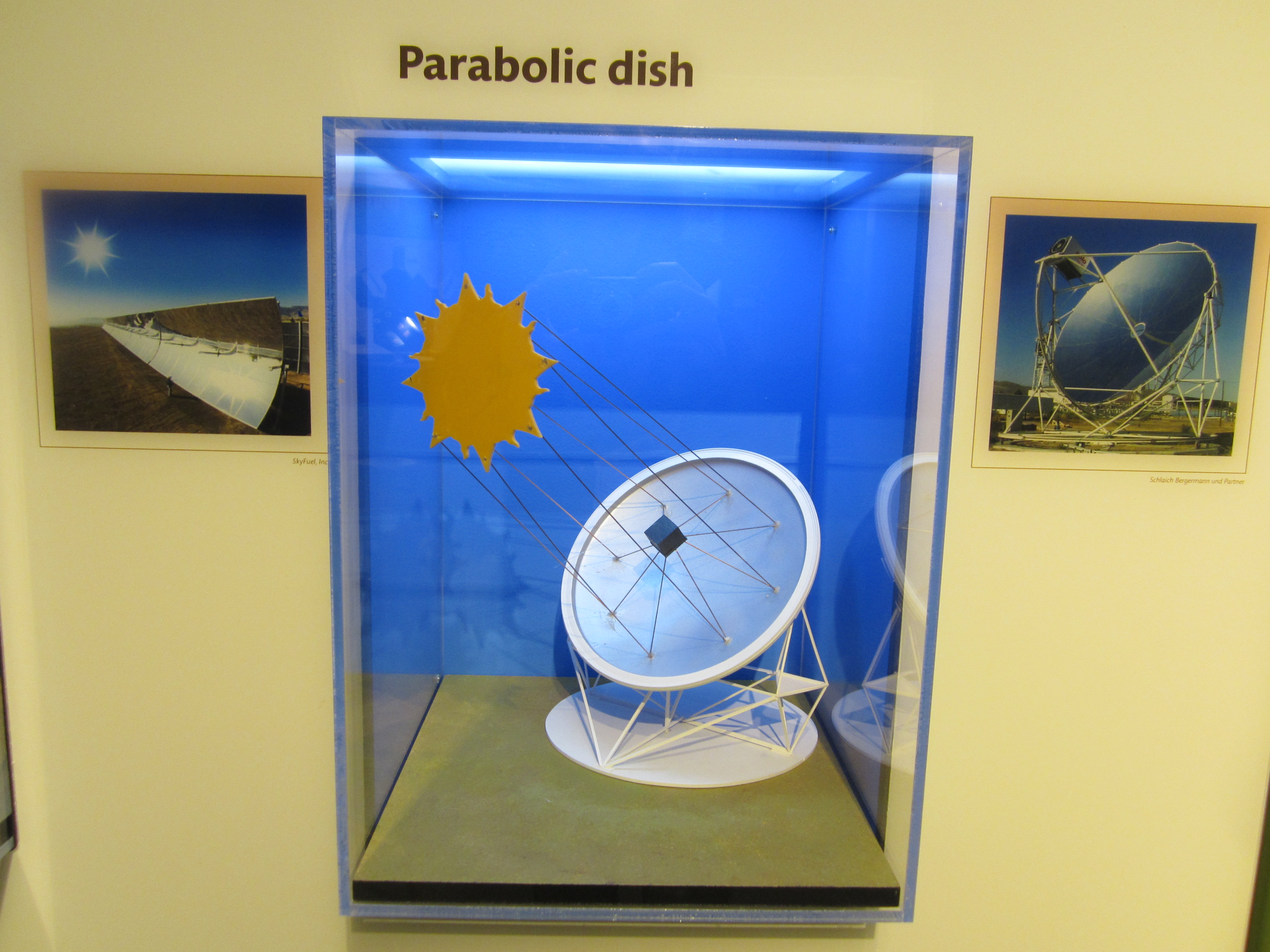
Sunlight can also be used to generate electricity without photovoltaics. Conventional power plants use their fuel to create heat to boil water. The steam from the boiling water turns the blades of a turbine, which generates electricity. Solar collectors use this same process, but the sun is the fuel source. They use mirrors to focus sunlight at a central point, generating enough heat to boil water. There are three main types of solar collectors: towers, troughs, and parabolic dishes. Solar collectors can be different shapes and sizes, but they all use mirrors to concentrate and intensify the sun’s energy.




The next exhibit I visited was Microrobotics Takes Flight. This exhibit was about the “RoboBee”. A RoboBee is a small robotic “insect” that a team from Harvard University is developing. They can be used for crop pollination, search and rescue missions, environmental exploration and military surveillance. The team still needs a tiny battery to power the RoboBee, but I think that it has huge potential. The RoboBee is very small, no bigger than a penny!


The last exhibit I visited on my journey through the Museum of science was Conserve at Home. I liked this exhibit the best out of the other three because you could interact with it and it was very playful. The exhibit had very interesting information about the uses of different resources. Conserving energy is a very important part of our everyday lives because it really makes a difference. Conserving energy not only saves money, but it also helps save our natural resources. The exhibit had some very interesting facts when you walked around and was set up to look like a house and it’s yard which I thought was adorable. Apparently the average American uses about 500 plastic bags every year! (But if you’re like my mom, she re-uses her Market Basket bags for everything….) A great alternative for plastic bags is to carry reusable bags. They’re fashionable and they’re better for the environment! Another great way you can conserve at home is to use energy efficient light bulbs and rechargeable batteries. One rechargeable battery can save about 800 disposable batteries!


When we think of conserving at home we usually think of recycling. And although that is a very important thing to do, their are a hierarchy of actions you could take before recycling. First you should start reducing the amount of waste you generate which is the most effective. Then you should reuse the materials by finding another use for them and then recycle all you can from whatever is left. Reducing may take more effort, but it can have a huge impact. The exhibit showed what the different recycling materials would turn into, which I thought was very interesting. A milk bottle could potentially be recycled into plastic decking for furniture. Soda cans can potentially be recycled into window frames, rain gutters, and new cans. Glass bottles can potentially be recycled into counter tops and glass jars. Steel cans can potentially be recycled into steel bicycles, paper clips, and new steel cans. Plastic water bottles and soda bottles can potentially be recycled into fleece and carpets!
Visiting the Museum of Science on Friday was a very fun experience because it brought back a lot of memories from when I used to go as a kid, but also because I learned a lot of useful information. I also liked that I could link the information that I learned at the museum back to the information that I learned in class about photovoltaics and energy resources!