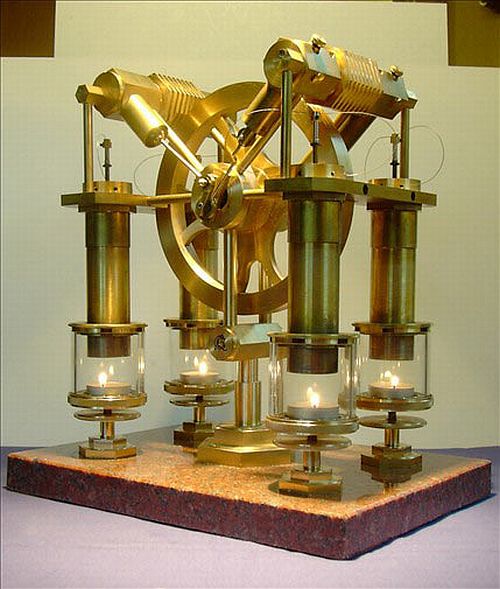
A Stirling engine is a heat engine operating cyclic compression and expansion of air or other gas, the fluid works at different temperature levels, such that a net conversion of heat energy to mechanical energy occurs.Originally conceived in 1816 by Robert Stirling designed as a first mover to rival the steam engine, in practice its use for home applications fell by almost a century. Stirling engines have high efficiency, when compared to steam engines, and easily to be applied to any source of heat. These advantages are making returns the interest in these engines, and their application in collectors systems of renewable energies.
Stirling engine powered by candels.
The Stirling engine is the only one capable of approaching (theoretically it reached) the maximum theoretical yield known as Carnot efficiency, so, as far as thermal performance engines are concerned, is the best choice.
ADVANTAGES
– The heat input is external, so that the combustion conditions are flexible.
– Works with any heat source, not only by burning, so you can use heat sources such as solar, geothermal, nuclear, biological, etc..
– Most Stirling engines have the mechanisms and the heat sink together, and therefore require less lubrication and last longer than alternative machines.
– The mechanisms are simpler than other alternatives machines, these is no need valves, the burner can be simplified.
– They can be built for run quietly without air consumption for submarine propulsion or operation in space.
– They are extremely flexible and can be used for cogeneration in winter and cooling in summer.
DISADVANTAGES
– Stirling engines require heat exchanger inlet and outlet, which must contain working fluid at high temperature and withstand the corrosive effects of the heat source and the atmosphere. This represents a rise in the price of the machine.
– Engines running with small thermal differentials are very large compared to the work done because of the exchangers.
– A Stirling engine can not start instantly, you must first “warm” the engine. This is true of all external combustion engines, but smaller than others such as the steam engine. It is best used in engines that require a constant speed.
STIRLING ENGINES IN THE XXI CENTURY
NASA itself is very interested in this type of converters has devoted significant energy and economic efforts in the development of applications that incorporate different engine models. In the Internet http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/tmsb/stirling/doc/stirling_animation.html we can see interesting animations of different engine models.
Solar Stirling engines have been used for decades, but has not reached mass market until 2010. Sean Gallagher, Vice President of Market Strategy and Regulatory Affairs for SES, says the reason they have taken so long to commercialize this technology, it is more logistical and economic problem that because of the technology itself.
In 2010 this technology for the first demonstration plant of 1.5MW in Maricopa Arizona is employed, using 60 disks SunCatcher Stirling technology. This plant is the first commercial example of this type of system and paves the way for the construction of solar plants with Stirling technology 1.5GW in California and Texas.
Until date today there are many plants that are operating in different geographical parts of the world, and marketing is available to anyone interested in using this wonderful technology.
Stirling disks, for generate energy.
NASA Stirling Engine
Striling Disk. Parts
Stirling Engines for submarines.
PELTIER EFFECT
Peltier effect is the production or absorption of heat caused by the passage of current through the contact of both metals or a metal and a semiconductor. The Peltier effect was discovered in 1834 by French physicist JCA Peltier emerged on the basis of the discovery of the German physicist TJ Seebeck in 1821.
The essence of the Peltier effect, involves passing a current from a continuous source of electricity through a circuit formed by two conductors of different nature to give one of its unions absorbs heat and releases it otherwise. The heat gives the hot spot will be the sum of the electrical energy supplied to the thermocouple and the heat absorbed by the cold source. These thermal elements are configured in this way, constitute a refrigerating machine.
Currently, one of its most common uses is as part of the CPU cooling computers.
It is also used in home dehumidifying equipment, because this system generates less noise than the compression system and is more compact.
http://www.ecotec2000.de/espanol/stir2.htm
http://www.sc.ehu.es/sbweb/fisica_/estadistica/termodinamica/stirling/stirling.html
http://eltamiz.com/2007/08/30/%C2%BFque-es-el-efecto-peltier/
http://www.ecured.cu/index.php/Efecto_Peltier
http://www.aulastecnopole.com/trabajos/Memoria_SAUL-FERNANDO.pdf